Since the servo valve itself is a product that combines electromechanical and hydraulics, and the servo valve and machine equipment form a complex system, when any link fails, how to effectively determine the cause of the failure and propose a solution is very important.
There are many ways to analyze servo valve failures. This issue mainly analyzes the static characteristics of the servo valve.
We will discuss the failure analysis of the servo valve from the following aspects: zero bias, internal leakage, hysteresis and resolution, flow gain and pressure characteristics, etc.
1. Zero bias failure performance: zero current exceeds the specified range. Possible consequences: safety protection position changes, and the failure insurance function fails to cause unknown failures.
2. Internal leakage failure performance: internal leakage exceeds the specified requirements, the valve is noisy and heats up significantly when working, causing the valve to fail to work stably. Possible reasons: The cleanliness of the oil does not meet the requirements, and it contains large metal particles. It washes the sharp edges of the valve core and the valve sleeve for a long time, causing the valve core to wear and become blunt. It is divided into normal use wear and abnormal use wear. Therefore, the hydraulic system using servo valves must ensure the cleanliness of the oil to ensure the normal use of the servo valve and extend its service life.

3. Hysteresis and resolution fault manifestation: slow valve core action response, stuck, and decreased dynamic response. Possible reasons: the oil filter in the valve is blocked, causing the oil to not smoothly enter the pilot stage; there are large particles of dirt between the valve core and the valve sleeve, causing the valve core to be stuck or stuck; the nozzle or throttling aperture of the nozzle flapper valve is very small, and large particles of dirt are blocked here. The above reasons will cause the servo valve hysteresis and resolution to be seriously out of tolerance or even the valve cannot move.
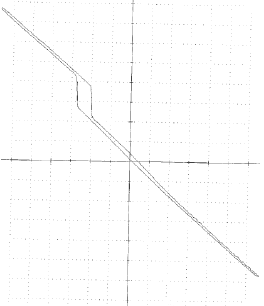
4. Flow gain fault manifestation: flow gain curve jumps suddenly.
Possible reasons: the torque motor feedback ball head is smaller than the valve core groove or hole. In this case, the torque motor needs to be replaced.
5. Pressure characteristic fault manifestation: internal leakage is out of tolerance. The valve core is worn and the valve core valve sleeve needs to be replaced.
Of course, the actual cause of the fault will be much more complicated than what we mentioned above. We need to combine the working conditions in actual applications and analyze specific problems in detail to improve our recognition ability.

