Hydraulic power packs are essential for driving various industrial machinery and systems. Installing these systems correctly is critical for the smooth operation and longevity of hydraulic equipment.
Table of Contents
- Step-by-Step Hydraulic Power Pack Installation Process
- Key Components of Hydraulic Power Pack Systems
- Essential Tips for Successful Installation
- Safety Measures During Installation
- Post-Installation Maintenance
Step-by-Step Hydraulic Power Pack Installation Process

The installation of a hydraulic power pack involves several steps. Here is a detailed guide on how to install it properly:
- Preparation: Before starting, ensure that you have all the required tools and components, including the power pack unit, hydraulic hoses, valves, pressure gauges, and electrical connections.
- Positioning the Power Pack: Place the hydraulic power pack in a stable and accessible location. Ensure there is enough space for the necessary connections and maintenance tasks.
- Connecting the Hydraulic Hoses: Connect the hydraulic hoses to the pump and valves. Double-check all connections for leaks to ensure proper fluid circulation.
- Electrical Connections: Connect the power supply to the motor according to the manufacturer’s specifications. Ensure that all electrical components are wired properly to prevent any electrical hazards.
- Reservoir and Fluid Filling: Fill the hydraulic reservoir with the recommended fluid. Verify the fluid level using the dipstick or sight gauge.
- Testing the System: Once all connections are made, power up the system and perform tests to ensure that the pump and valves are working correctly. Check for leaks and proper fluid flow.
Key Components of Hydraulic Power Pack Systems
Understanding the main components of a hydraulic power pack is essential for a successful installation. Here’s a breakdown of the key elements:
| Component | Description | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Hydraulic Pump | The pump converts mechanical energy into hydraulic energy. | Generates hydraulic flow and pressure. |
| Hydraulic Reservoir | A container that holds the hydraulic fluid. | Stores the hydraulic fluid and helps in cooling. |
| Control Valves | Valves regulate the flow and direction of hydraulic fluid. | Directs fluid to the actuators for operation. |
| Pressure Relief Valve | A safety feature that limits system pressure. | Prevents system overload by diverting excess pressure. |
Essential Tips for Successful Installation
Here are some helpful tips to ensure a smooth installation of your hydraulic power pack:
- Check for Compatibility: Make sure all components are compatible with your system, including the pump, motor, and control valves.
- Ensure Proper Ventilation: Good ventilation is essential to prevent the power pack from overheating during operation.
- Use High-Quality Hydraulic Fluid: Always use the fluid recommended by the manufacturer to ensure optimal performance.
- Proper Alignment: Ensure that all components, especially the pump and motor, are properly aligned to prevent undue wear and tear.
- Secure Connections: Ensure all hydraulic hoses and electrical connections are tight to prevent leaks and electrical failures.
Safety Measures During Installation
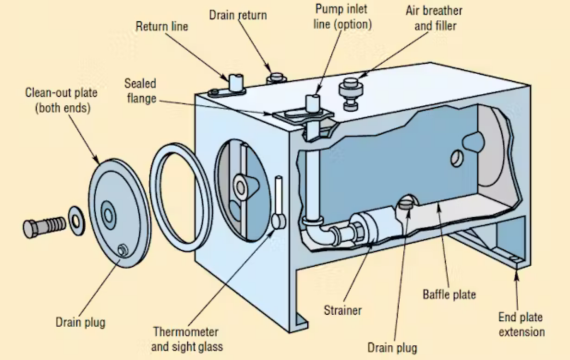
During the installation of hydraulic power packs, safety is paramount. Here are some crucial safety measures to follow:
- Wear Protective Gear: Always wear gloves, goggles, and other personal protective equipment to protect against fluid leaks and electrical hazards.
- Follow Manufacturer Guidelines: Adhere to the manufacturer’s instructions for all aspects of the installation process to avoid system malfunctions.
- Test for Leaks: After installation, check all hydraulic and electrical connections for leaks and ensure that the system is functioning properly before use.
Post-Installation Maintenance
Once the hydraulic power pack is installed, regular maintenance is crucial to keep the system running smoothly. Follow these post-installation maintenance guidelines:
- Inspect Fluid Levels: Check the fluid levels regularly and top up as needed to avoid system damage.
- Monitor Pressure: Keep an eye on the pressure readings to ensure they stay within the manufacturer’s recommended range.
- Clean and Replace Filters: Clean and replace filters periodically to prevent contamination in the hydraulic system.

